 PLATFORMS
SOLUTIONS
BLOGS
CONTACT
☰
PLATFORMS
SOLUTIONS
BLOGS
CONTACT
☰
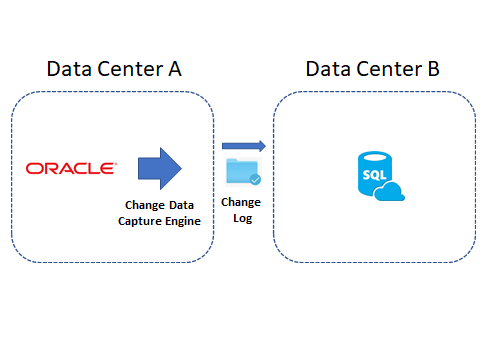
In this blog we are going to demonstrate how to replicate an Oracle table to a SQL Server database
using ENZO DataZen.
DataZen is a replication technology that can detect changes made to any source system through a proprietary
Change Data Capture (CDC) engine. Because the CDC engine built into DataZen is universal by design, it can
detect changes (adds, updates, and deletes) regardless of the source system (relational, no-sql, or any API exposed through ENZO Server
or an ODBC driver).
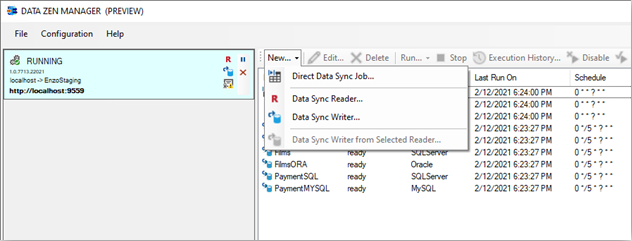
There are three kinds of Sync jobs in DataZen: Jobs Readers, Job Writers, and Direct Jobs.
ENZO DataZen replicates data using an eventual consistency model. This means that the data at the target system will eventually match data at the source.
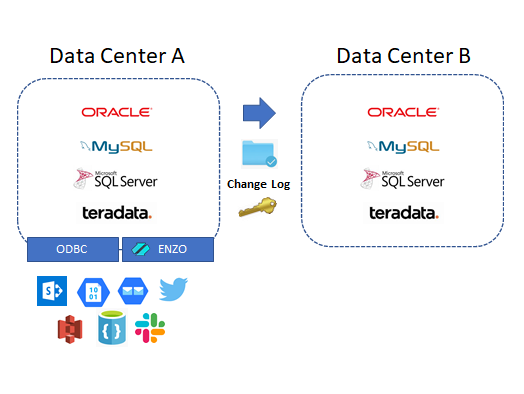
DataZen can natively connect to any relational database through an ODBC driver.
In addition, certain scripts can be automatically generated for some of
the well-known database platforms (Oracle, MySQL, Teradata, and SQL Server).
In addition to using ODBC drivers, DataZen can also access virtually any platform directly using
SQL commands through Enzo Server without the need for an ODBC driver. For example, if you currently
have ENZO Server configured to access SharePoint Online, you can instantly replicate SharePoint list data to any
other system with DataZen.
We will be using Oracle as the source system, and will demonstrate how to setup a Direct Job replication. As discussed previously, Direct Jobs combine both a Job Reader and a Job Writer into a single operation for simpler replication topologies.
To create a Direct Job, start DataZen, click on the desired Agent (at least one agent must be registered),
and select NEW -> Direct Data Sync Job from the context menu.
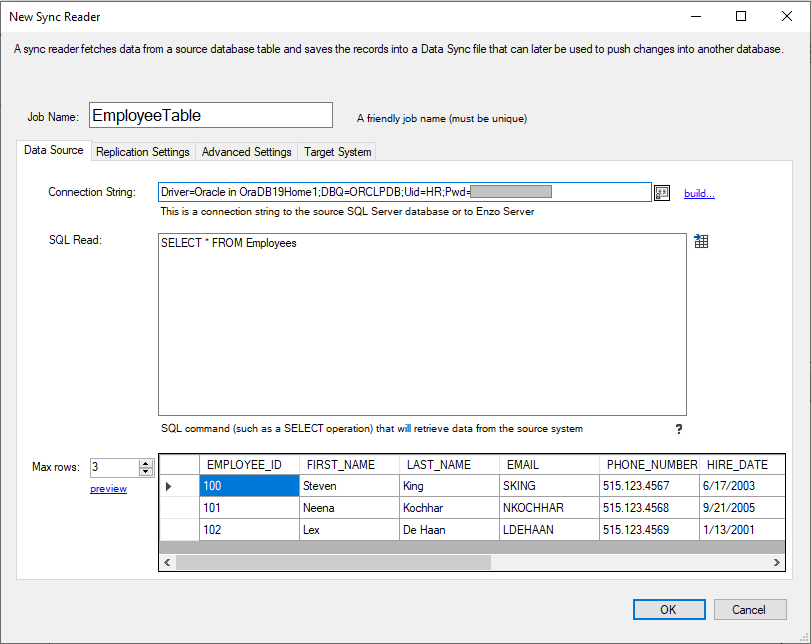
Enter a Job Name, and specify a connection string to the source system. You can click on build...
to help construct a valid connection string. Enter a valid SQL statement for Oracle and click on
preview. This is necessary to ensure the connection string is valid and to help build
the rest of the job.
The statement specified will be wrapped by another SELECT operation so that only a few records are returned at a time. If you enter a complex SQL command that cannot be wrapped into a SELECT operation (such as if you call a stored procedure), check the Bypass TOP/LIMIT N option under the Advanced Settings tab to disable heuristics.
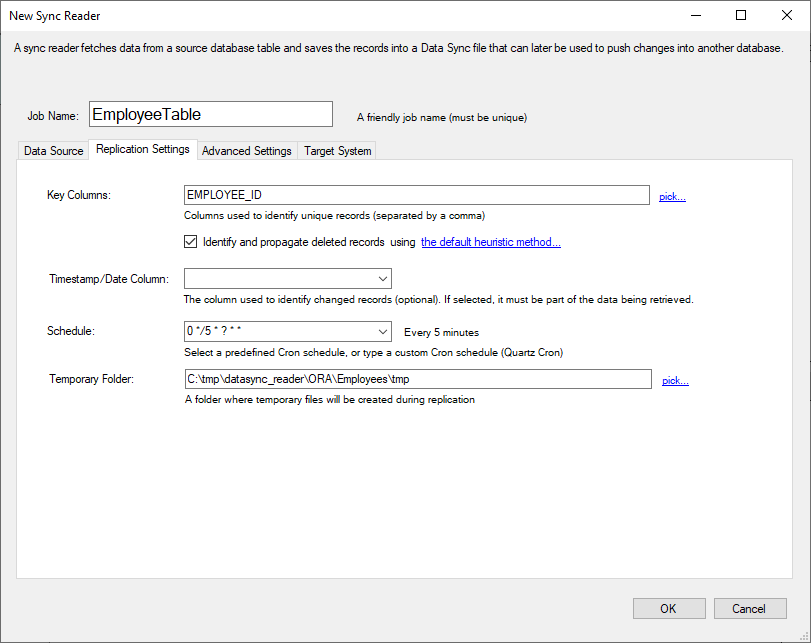
Click on the Replication Settings tab and select a Key field (in this example, we picked EMPLOYEE_ID).
You may select more than one field as the Key field if needed. To propagate delete operations, check the
Identify and propagate deleted records.
Choose a replication schedule (as a Cron expression), and select a folder in which the Sync files will be created.
Choosing a Timestamp/Date Column speeds up the identification of modified records significantly. It is only available if the SQL command is a SELECT operation.
Click on the Target System tab and specify a connection string. In this example, we are using a SQL Server Native connection; as a result the High Performance MERGE Operation option is available (this operation offers signficant performance advantages for SQL Server).
Enter a target table in the target database. The table should be in the following format for SQL Server: [schemaname].[tablename].
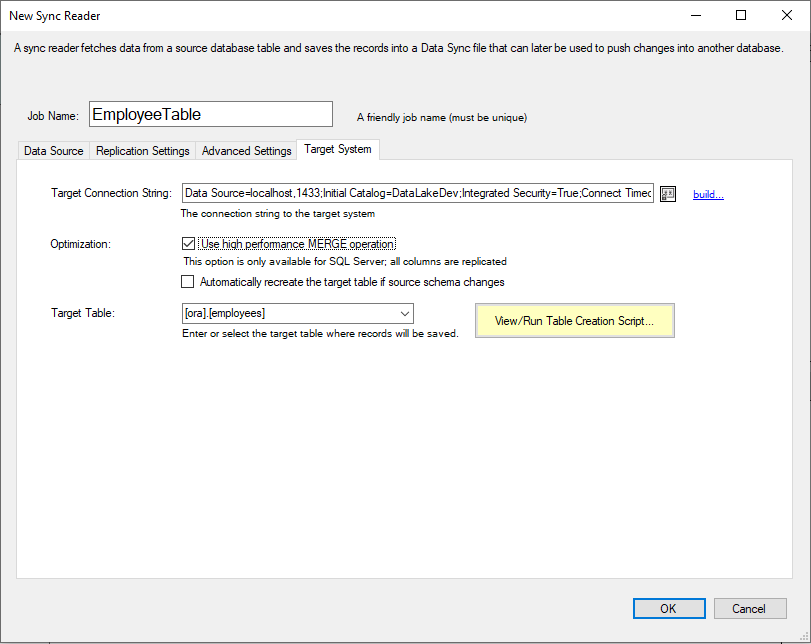
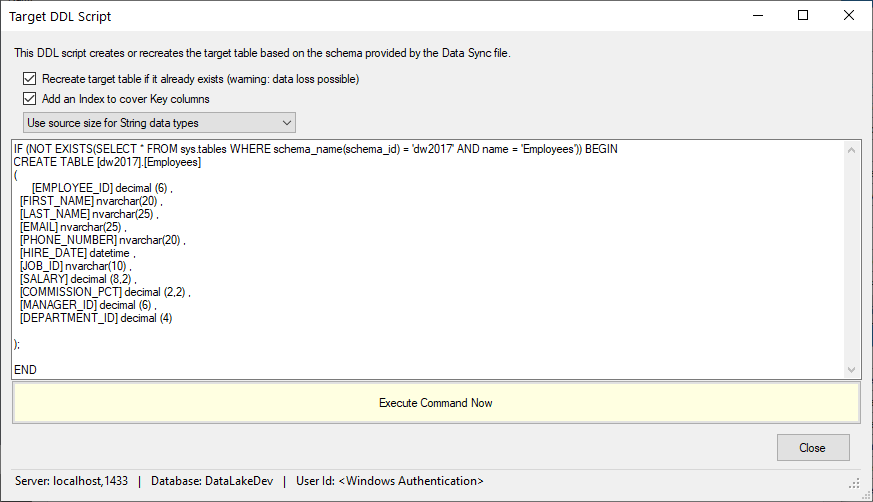
To minimize any errors in the creation of the target table, including possible data type convertion issues, click on the View/Run Table Script button. A screen will allow you to review the SQL command used to create the target table and execute the command that will create the target table. Enzo will automatically select the correct data type for the selected target system.
It is highly recommended (required when the targer system is Oracle or MySQL) to choose the Add an index to cover Key Columns. If the target system is Teradata, use a PRIMARY KEY on the Key Columns.
Click on Execute Command Now to create or recreate the target table.
Click Close and then click OK to create the Direct Job.
If you have selected a Schedule (Cron Expression) the job will start immediately; otherwise you will need to click on the Start icon for the job. The example provided selects records from a small table in Oracle (107 records in all), so the complete operation takes just a few seconds.
You can see the details of the operation (read and write) from the Output Log at the bottom of the screen.
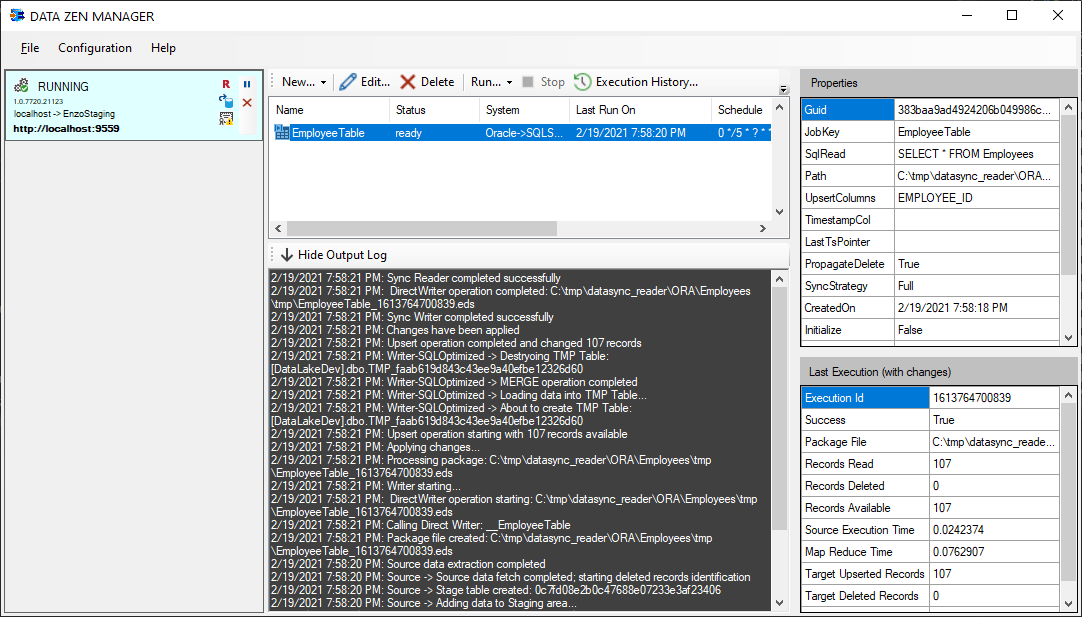
The Last Execution window shows the last available operation statistics that actually performed a change. The following key information is available:
This blog shows you how you can easily replicate database tables across two different relational database engines,
specifically from Oracle to SQL Server. DataZen provides the necessary logic to make replication quick and
easy, including data type mapping, automatic retries, and advanced heuristic options for large tables.
To try DataZen at no charge,
download the latest edition of DataZen on our website.
Integrate data from virtually any source system to any platform.
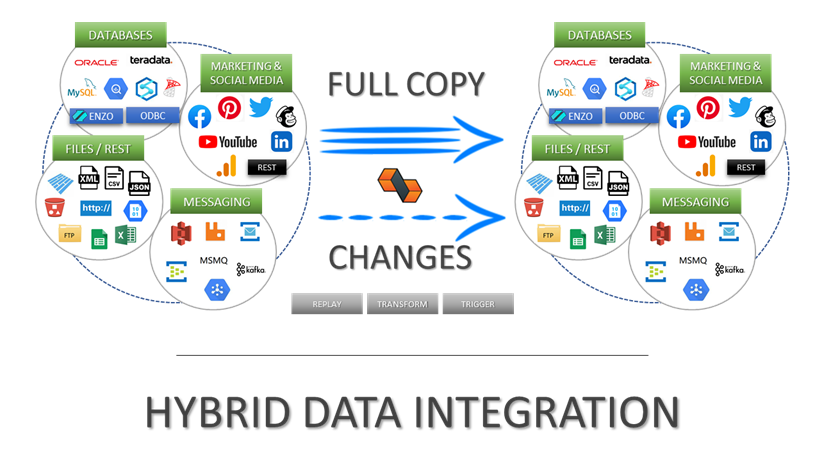
Support for High Watermarks and fully automated Change Data Capture on any source system.
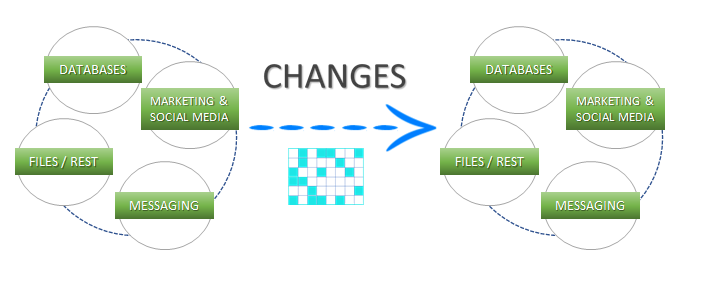
Extract, enrich, and ingest data without writing a single line of code.
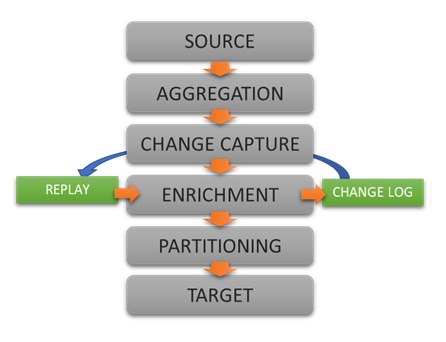
To learn more about configuration options, and to learn about the capabilities of DataZen,
download the User Guide now.
© 2023 - Enzo Unified